$ cat announce.txt
-
Course evaluation is currently… 43%.
-
Please do the evaluation!
-
ASST3.3 targets and test updates will be released soon.
-
Please attend the distinguished lecture tomorrow! 3:30PM in Clemens 120.
-
Office hours tomorrow will end at 3:30PM.
-
Hari Balakrishnan is an extremely famous systems and networking researcher and the talk is about an app and will be quite interesting.
-
You might also discover what a good driver I am…
-
Shameless Plug
If you are around next year, please apply to be a UTA for the new freshman seminar! Here’s the link: https://goo.gl/forms/kJV3VBs9gX. Or here:
Performance and Benchmarking: Questions?
Statistics: That’s Math, Right
Computer systems researchers have a somewhat tortured relationship with statistics and math. (Many of us are computer systems researchers because we weren’t smart enough to do mathematics.)
-
On a good day: "I’ll rerun my experiment a few times and compute an average."
-
For extra-special bonus points: "I’ll put error bars on my graph."
First, Predict
Before performing an experiment and collecting data it is helpful to make predictions.
-
One way to do this is to draw sketches of the graphs you expect to produce.
-
After collecting real results you can compare them against your predictions as a way of developing intuition about your system.
-
(Predictions about simple cases are also good ways to validate models and simulators.)
Understand Your Data
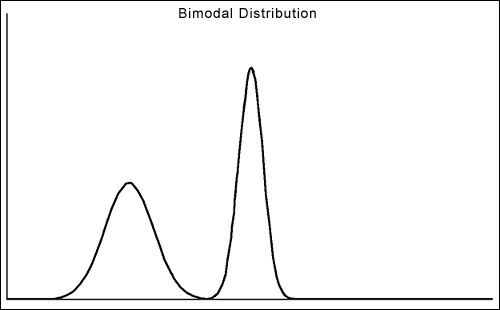
Beware the premature use of summary statistics--means, medians, etc.
As an example, the following data from two experiments could have the same mean and median:
|
|
Clearly they would have very different implications for performance improvement, so examine your raw data!
Love Your Outliers
-
They may just be weird remnants of your measurement harness.
-
They may have a lot more to tell you.
-
Understand them either way.
Deciding What to Improve
Improve the slowest part, right?
-
(Even if it were this simple, getting programmers to work on any one specific thing can be hard. Frequently they decide to optimize something simply because "they want to".)
-
foowhich takes 5 minutes to execute. -
barwhich takes 5 seconds to execute.
Clearly you should immediately get to work improving foo, right?
Why Not foo?
What two elements have we missed in our overly-simplistic decision?
-
Significance: how much does
foomatter? -
Difficulty: how hard is it going to be to improve
foo?
-
Significance, so let’s start there.
Amdahl’s Law
The impact of any effort to improve system performance is constrained by the performance of the parts of the system not targeted by the improvement.
-
Reducing the execution time of
foofrom + 5 minutes → 1 minute. -
Reducing the execution time of
barfrom + 5 seconds → 4 seconds.
foo is better:-
absolutely (4 minutes v. 1 second) and
-
proportionally (80% v. 20%).
foo
Not So Fast (Pun Intended)
-
Reducing the execution time of
foofrom + 5 minutes → 1 minute. -
Reducing the execution time of
barfrom + 5 seconds → 4 seconds.
But what if our program spends 95% of its time running bar but
only 0.1% running foo?
-
foospeedup: 0.001 * 240 seconds = 0.24 seconds. -
barspeedup: 0.95 * 1 = 0.95 seconds.
This is why server performance geeks take a month vacation every time they trim one instruction off of a hot path.
Amdahl’s Law
Even more colloquially:
Ignore the thing that looks the worst and fix the thing that is doing the most damage.
And the unfortunate corollary to Amdahl’s law:
The more you improve one part of a system the less likely it is that you are still working on the right problem!
Performance and Benchmarking: Questions?
Hints for Computer System Design
Systems Are More Complicated Than Algorithms
(Don’t tell Atri.)
-
"The external interface (that is, the requirement) is less precisely defined, more complex, and more subject to change."
-
"The system has much more internal structure, and hence many internal interfaces."
-
"The measure of success is much less clear."
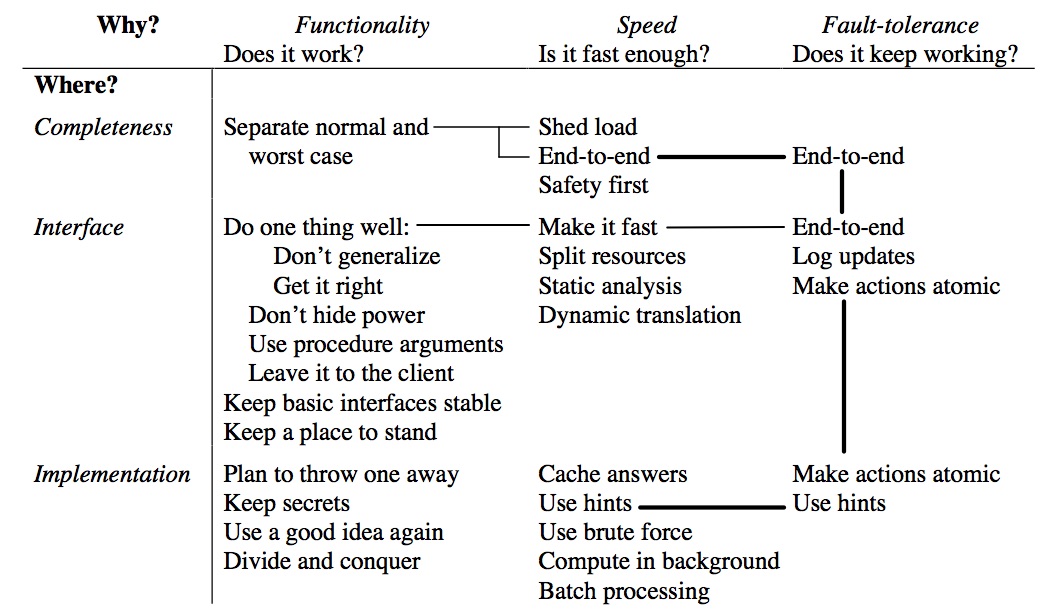
I have designed and built a number of computer systems, some that worked and some that didn’t. I have also used and studied many other systems, both successful and unsuccessful. From this experience come some general hints for designing successful systems. I claim no originality for them; most are part of the folk wisdom of experienced designers. Nonetheless, even the expert often forgets, and after the second system [6] comes the fourth one.
Three Goals
-
Functionality
-
Speed
-
Fault-tolerance
-
Ensuring completeness
-
Choosing interfaces
-
Designing implementations
Summary of the Hints
To The Paper
Next Time
-
Butler Lampson on how to make things fast.
Next Time
-
Making Linux run fast on many cores.